Goat
Introduction
|
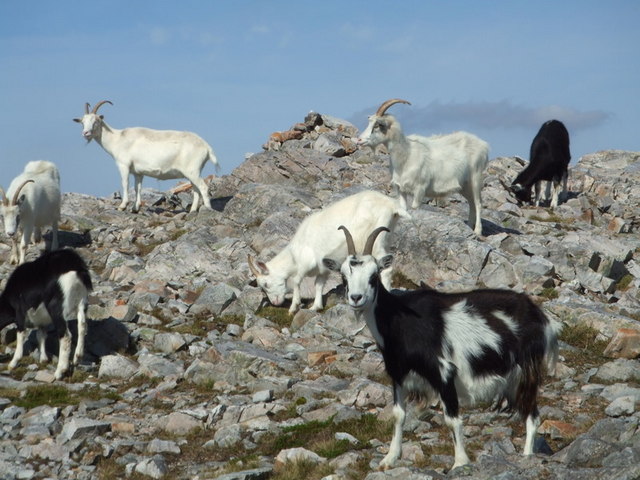
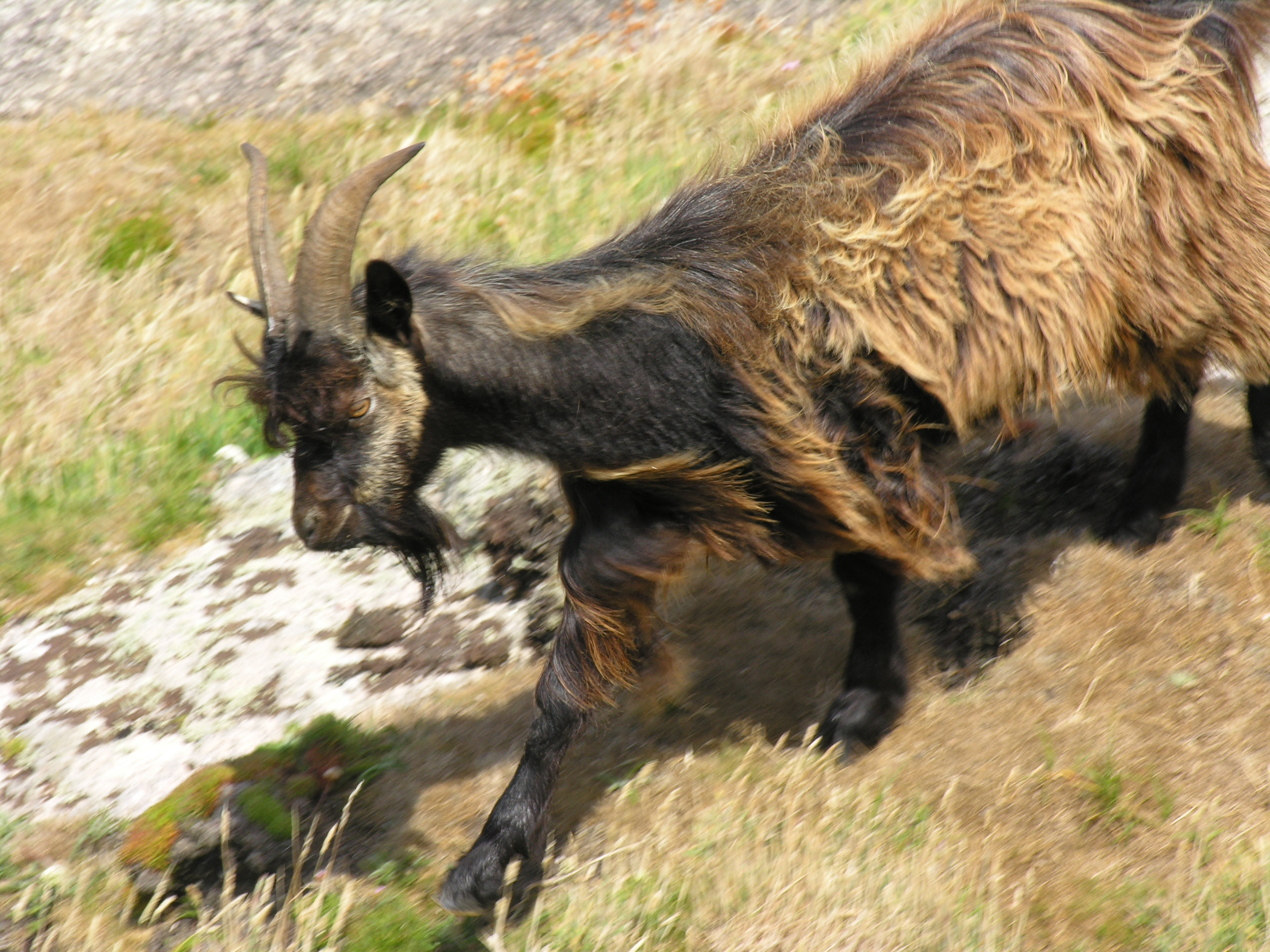
On this page... (hide) Goats were domesticated by humanity; they are likely to have fled into the wild, reestablishing themselves in 'Souls territories. Life expectancy for goats is between 15 and 18 years. Most goats naturally have two horns, of various shapes and sizes depending on the breed. Goats have horizontal, slit-shaped pupils. Because goats' irises are usually pale, their contrasting pupils are much more noticeable than in animals such as cattle, deer, most horses and many sheep, whose similarly horizontal pupils blend into a dark iris and sclera. Top Speed: 10mph / 17km per hour |
1. Speech
According to our Speech Guide, this creature speaks Low Speech naturally. It is therefore not able to communicate with Luperci. This creature is listed as having the ability to learn some limited comprehension of high speech, but generally will never be able to speak it.
2. Uses
- Food: --
- Meat: Goat meat has been described as having a savory, strong, gamey flavor that is a little sweeter than lamb but less-so than beef. Depending on the size of the goat, a carcass could yield up to (18 kg) 40 lb of lean meat.
- Milk: On average, a doe in her prime will produce about 2.7 kg - 3.6 kg (6 - 8 lb) of milk a day over a 305-day lactation period. If milked continuously, a doe may continue to give milk past 305 days without having been bred, but the amount produced at each milking gradually decreases closer to the natural end of her lactation cycle.
- Cheese: --
- By-Products:
- Pelts and hides: As with any animal, hides and pelts can be made from goats.
- Goatskin: Tanned goatskin can be used in the development of a number of things, including leather and parchment.
- Fiber: The fibers of some longer-haired goats can be trimmed or brushed from the animal and spun into yarn. A single long-haired goat can produce 4 ounces of cashmere annually.
- Intestines: The intestines of goats have traditionally been used to make catgut.
- Horns and Bones: Goat horns, which are hollow, can be used as vessels, containers, or tools while bones can be used to make fishing hooks, needles, tools, and ornamentals.
- Glue: Made from boiling connective tissues (skin, tendons, bones, hooves, etc.). Animal glue has a number of uses ranging from adhering items together to preserving hairstyles.
- Manure: Manure can be composted into fertilizer but, historically, was used for fuel.
- Pelts and hides: As with any animal, hides and pelts can be made from goats.
- Companionship: --
- Labor: Goats can be trained to pull carts (maximum load of 2x their body weight) and/or carry packs (maximum load of 25% their body weight).
3. Types
3.1 Goat↪ Domestic Goat (Capra aegagrus hircus) |
| Useful Information |
|
| Quick Facts |
|
| Appearance |
4. Additional Resources
4.1 Icons






5. Sources


